Advanced Analysis (FEA)
ENGINEERING SPECIALTY
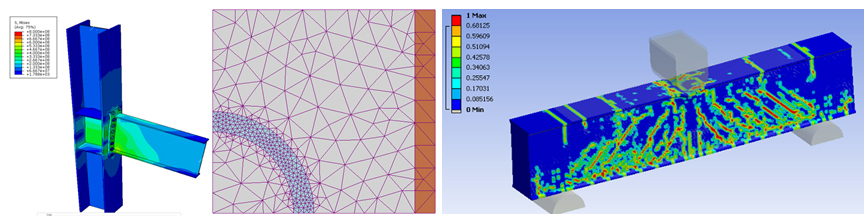
About Finite Element Method Analysis
The finite element method (FEM) is a numerical technique for finding approximate solutions to boundary value problems for differential equations. It uses variational methods (the calculus of variations) to minimize an error function and produce a stable solution. Analogous to the idea that connecting many tiny straight lines can approximate a larger circle, FEM encompasses all the methods for connecting many simple element equations over many small subdomains, named finite elements, to approximate a more complex equation over a larger domain.
Application
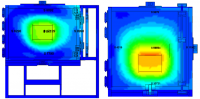
In general, although it is an excellent analysis tool, FEM is hard to apply to a whole building because of the time required and complexity involved. However, it is very powerful method when it goes beyond the assumptions of regular structural analysis. For instance, it is commonly used for steel connections, deep beams, and complex shape elements when needed.
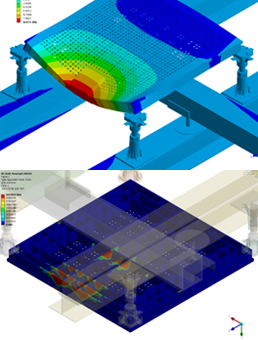
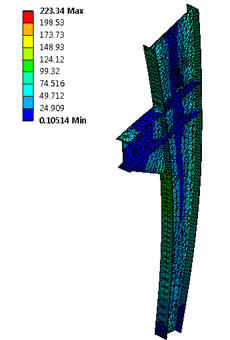
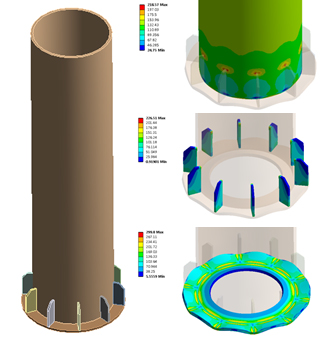
- Static Analysis – check serviceability and failure shape predictions using FEM and full 3D mathematical modeling
- Nonlinear Behavior Prediction – predict and analyze structural behavior using nonlinear material properties
- Connection Analysis – check structural stability in suspicious connections
- Buckling Analysis – buckling analysis in steel elements